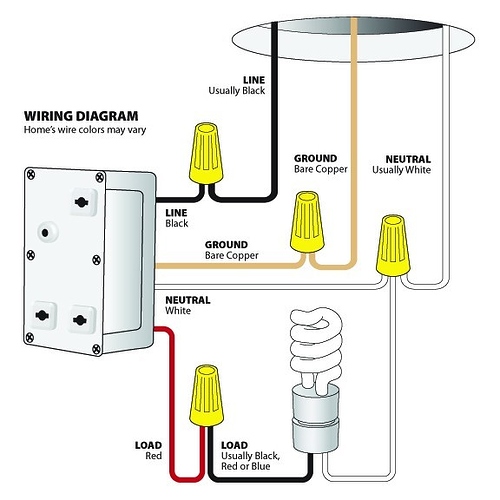
Line wires carry electricity from the power source to the switch, while load wires transmit power from the switch to the electrical device. Understanding the difference between line and load wires is crucial for safe electrical work.
Electricity flows into our homes and powers our appliances and lights through a well-orchestrated system of wires. To ensure this system works safely and efficiently, it’s important to distinguish between two key types of wires: the line and the load.
The line wire is the conductor that brings electricity into a switch or outlet, serving as the initial point of contact for electrical current. Conversely, the load wire takes the role of the exit pathway, carrying electricity away from the switch to the appliance or fixture in need of power. Often found in the setup of circuit breakers, outlets, and switches, these wires are vital in controlling the flow of electricity and must be connected correctly to prevent electrical hazards. Determining the specific function of each wire can be critical for troubleshooting electrical issues and performing any necessary repairs or installations.
Credit: www.quora.com
Introduction To Electrical Wiring
Understanding the basics of electrical wiring is crucial for safety and efficiency in your home. Electrical circuits are the lifeline of household functionality, and knowing the difference between line and load wires is essential for any DIY project or general knowledge about your home’s electrical system.
Basics Of Electrical Circuits
An electrical circuit consists of various components that create a pathway for electricity to flow. Each component plays a specific role in ensuring power reaches your appliances safely. Let’s break down these components into more manageable pieces:
- Power Source: This is where the electricity originates, like your home’s breaker box.
- Conductors: Usually wires, these carry electricity from the source to your devices.
- Load: The appliance or fixture that uses the electrical power to operate.
- Switches: Control points that allow you to turn electricity to the loads on or off.
- Protective Devices: Such as fuses or circuit breakers, these prevent overloads.
Role Of Wires In Power Distribution
Electricity travels through wires to power up our homes and devices. Different types of wires have different roles:
| Wire Type | Function |
|---|---|
| Line Wires | Carry power from the source to the switch or outlet |
| Load Wires | Transport power from the switch or outlet to the device or appliance |
| Neutral Wires | Complete the circuit by returning unused power to the source |
| Ground Wires | Enhance safety by directing excess electricity to the ground |
Distinguishing between line and load wires is vital. The line wire brings electricity into an outlet or switch, and the load wire takes it out to the end device. Remembering this can prevent potential hazards and improve the effectiveness of your electrical system.
Dissecting Line Wires
Understanding electrical systems requires a closer look at line wires. These wires play a pivotal role in power distribution. Let’s dive into the specifics.
Characteristics Of Line Wires
Line wires, often referred to as hot wires, carry electricity from power sources. Being a primary conductor, it is crucial for circuit operation.
- Insulation Color: Typically black or red.
- Electric Potential: Carry high voltage compared to neutral or ground wires.
- Connection Point: Directly connected to circuit breakers.
Safety comes first with line wires. They should never be touched while handling electrical components.
Common Uses Of Line Wires In Circuits
Line wires find their importance in various applications within circuits.
| Application | Function |
|---|---|
| Power Outlets | Provide voltage to the outlets. |
| Switches | Control power flow to lights or devices. |
| Appliances | Electricity source for functioning. |
Recognition and handling of line wires require knowledge and care. Utilizing them effectively is key for a safe and functional electrical system.
Unraveling Load Wires
In this section, we’ll dive into the world of load wires. Load wires are crucial in an electrical system. They ensure that power gets to where it needs to go. From keeping your fridge running to lighting up your bedroom, load wires play an essential role in our daily lives. Let’s break down what load wires are and how they connect to various devices.
Defining Load Wires
Load wires carry electricity to devices and appliances. They complete the circuit by bringing power from the source. The load itself could be anything that consumes electricity. This wire is usually on the downstream side of a circuit. We can find it leaving switch boxes or outlets.
Typical Connections And Appliances
Different appliances have unique wiring needs. Each draws a certain amount of power to function properly.
- Lights - Load wires connect to light fixtures. They power them up.
- Receptacles - Load wires plug into these outlets. They supply power for you to use.
- Switched Outlets - Here, load wires interact with switches. They turn appliances on or off.
In homes, load wires mostly connect to:
| Device | Function |
|---|---|
| Fridge | Keeps food cold |
| A/C Unit | Cools down rooms |
| Washer | Cleans clothes |
| Dryer | Dries clothes |
-max_bytes(150000)-strip_icc()/line-and-load-connections-1152729-hero-3c69852fd05843b3b1eaa1051e9c6065.jpeg)
Credit: www.thespruce.com
Key Differences And Comparison
Understanding the roles of line and load wires matters. It can prevent electrical mishaps. Let’s compare their characteristics.
Voltage And Current Characteristics
Line and load wires carry different voltages. The line wire connects the power source. It carries a full voltage. The load wire completes the circuit to your device. It carries a reduced voltage after the load.
| Line Wire | Load Wire |
|---|---|
| Full voltage from power source | Reduced voltage to device |
| Connects to circuit breaker | Connects from device to breaker |
In an electrical panel, line wires connect to breakers. Load wires link from breakers to outlets or fixtures.
- Line wire: Always live when circuit is active.
- Load wire: Current flows when device is on.
Safety Implications Of Mistaken Identity
Mixing up line and load can be dangerous. It might damage appliances or cause electric shock. Keep them straight to stay safe.
- Wire color helps identify line and load.
- Line is usually black, load might be red or white.
- Use a voltage tester to confirm before you touch.
Remember: Always turn off power before working with wires. Call a professional if unsure.
Practical Guide To Identification
Identifying the difference between line and load wires is crucial in any electrical DIY project. This guide simplifies the process, aiding in safe and successful outcomes.
Color Coding And Markings
Color coding forms the backbone of wire identification. In general, black wires are considered hot, carrying power from the breaker. They often represent the line wires. White or gray indicates neutral wires, connected on the load side, termed load wires. However, colors can change based on local codes.
- Never assume colors without testing; use a voltage tester.
- Line wires connect to the breaker or fuse.
- Load wires connect to the device, such as an outlet or switch.
Some wires have markings or stripes that aid in identification. A wire with a green screw is often the ground wire, essential for safety.
Tips For Safe Handling During Diy Projects
Electrical work demands attention to safety. Follow these tips to ensure a secure DIY experience:
- Power off: Always shut off the main power at the breaker box.
- Use proper tools: Equip yourself with insulated pliers and screwdrivers.
- Double-check: Confirm the power is off with a non-contact voltage tester.
- Label wires: Before disconnecting, label each wire with tape to remember the connections.
- Wear safety gear: Rubber-soled shoes and safety goggles are a must.
- Consult a professional if unsure.
Remember, identifying your line and load wires correctly is essential. Use this guide to approach your projects with knowledge and care.
Industry Standards And Codes
Understanding the difference between line and load wires is crucial for safe electrical work. Strict guidelines, known as industry standards and codes, ensure this practice remains consistent and safe worldwide. Compliance with these standards is a must for any electrical installation or repair.
National Electrical Code (nec) Guidelines
The National Electrical Code (NEC) is a widely adopted set of safety standards for electrical wiring in the United States. It sets the benchmark for the electrical industry and helps protect people and property from hazards associated with electrical installations. The NEC provides clear directives for identifying line and load wires:
- Line wires, or ‘hot’ wires, carry electricity from the power source.
- Load wires take power from the line wires to the electrical device.
- Color coding of insulation is often used for identification.
- Grounding and bonding requirements must be met.
- Wire size and type must suit the electrical load.
The NEC is revised every three years, ensuring that the guidelines reflect the latest safety practices and technological advancements.
International Wiring Color Standards
Around the world, the colors of wires inside electrical systems indicate their function. International standards can differ by country, but they play the same role as NEC in the US—promoting safety and clarity. Here is an overview of color standards:
| Region | Line (Live or Phase) Wire Color | Neutral Wire Color | Ground (Protective Earth) Wire Color |
|---|---|---|---|
| Europe (IEC) | Brown or Black | Blue | Green with Yellow Stripe |
| North America (NEC) | Black, Red, or Blue | White or Gray | Green or Green with Yellow Stripe |
| Australia & New Zealand | Red or Brown | Blue | Green with Yellow Stripe |
These standards facilitate international cooperation and help prevent confusion for electricians working on diverse equipment or in different regions.
Credit: getorro.com
Conclusion
Understanding the roles of line and load wires is crucial for any electrical project. By grasping their differences, you ensure safety and functionality within circuits. For DIY endeavors or when discussing with professionals, this knowledge is key. Keep these insights in hand and embark on electrical tasks with confidence.
I’m Robert M. Payne, a passionate enthusiast for turning houses into dream homes. With a knack for DIY projects and a keen eye for design, I’ve dedicated myself to sharing my knowledge and experiences in the realm of home improvement.
As a seasoned homeowner and avid DIYer, I understand the challenges and joys that come with transforming living spaces. Through Myhomemyworld, I aim to inspire and guide fellow homeowners on their journey to creating spaces that reflect both functionality and style.
Cheers to creating spaces that truly feel like home.
Connect with me in facebook
